Terms of Use
YOU EXPLICITLY UNDERSTAND AND AGREE THAT USE OF THE API AND CONTENT IS AT YOUR SOLE RISK AND THAT PROVIDED CONTENT IS PROVIDED "AS IS." PLX DEVICES INC. SHALL NOT BE LIABLE FOR DIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES RESULTING FROM ANY LEGAL THEORY INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, LOST PROFITS, DOWNTIME, GOODWILL, DAMAGE, INJURY TO PERSONS, OR REPLACEMENT OF EQUIPMENT AND PROPERTY DUE TO IMPROPER INSTALLATION, INTEGRATION AND/OR MISUSE OF ANY PLX DEVICES INC.'S PRODUCT(S) AND DOCUMENTATION.
Overview
The PLX Kiwi Wifi is an OBD-II to IEEE 802.11 wireless Ethernet adapter.
The PLX Kiwi Bluetooth is an OBD-II to Bluetooth adapter.
The Kiwi iMFD Adapter is an addon adapter for the Kiwi 2 Wifi that offers iMFD serial data support in addition to available OBD-II information.
Products

|

|
|
Kiwi 2 Wifi / Kiwi 2 Bluetooth
|
iMFD Adapter
|
Block Diagram
The Kiwi 2 Wifi and Kiwi Bluetooth are equivalent in functionality. Both the Kiwi 2 Wifi and Kiwi Bluetooth have a built-in OBD interface. For additional PLX iMFD sensor support, the iMFD adapter can be connected to the Kiwi 2 Wifi and programmatically accessed via an internal mode selector switch.
Kiwi 2 Wifi/Kiwi Bluetooth

Kiwi 2 Wifi with iMFD Adapter
Connecting to Kiwi
To communicate with the Kiwi Wifi, connect to the following IP address and port:
SSID: PLXDevices
IP: 192.168.0.10:35000
For the Kiwi Bluetooth, pair to the device with the following pairing code:
Device Name: PLXDevices-XXXX
Pairing Code: 1234
Setting Sensor Mode (iMFD Adapter)
With the iMFD Adapter connected, there are two modes of operation: OBD mode and iMFD mode. In OBD mode you have access and control of the OBD interface. In iMFD mode, you have access to the PLX iMFD serial stream. These modes can be switched by sending a '+' or '-' ASCII character.
OBD Mode
Send the ASCII character '+' (Decimal value = 43, Hex value = 2B) to set the mode to OBD.
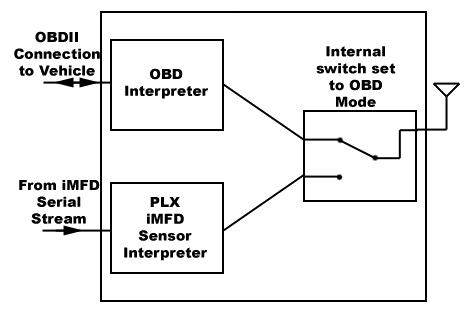
iMFD Mode
Send the ASCII character '-' (Decimal value = 45, Hex value = 2D) to set the mode to iMFD.
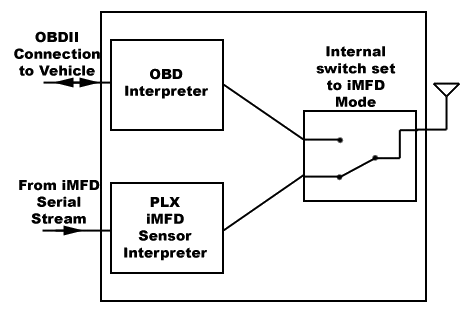 Communicating with Kiwi
Communicating with Kiwi
Communicating with the Kiwi Wifi is made by writing and reading ASCII values to and from the TCP stack.
Communicating with the Kiwi Bluetooth is made by reading and writing ASCII values via a serial stream.
Request Formats
OBD Mode
To signify that the Kiwi Wifi or Kiwi Bluetooth is ready to process commands, the device will output a greater-than sign (>).
The Kiwi Wifi and Kiwi Bluetooth supports ten diagnostic modes as defined in the SAE J1979 standard:
|
Test mode
|
Description
|
|
01
|
Show current data
|
|
02
|
Show freeze frame data
|
|
03
|
Show diagnostic trouble codes
|
|
04
|
Clear trouble codes and stored values
|
|
05
|
Test results, oxygen sensors
|
|
06
|
Test results, non-continuously monitored
|
|
07
|
Show 'pending' trouble codes
|
|
08
|
Special control mode
|
|
09
|
Request vehicle information
|
|
0A
|
Request permanent trouble codes
|
Requesting information can be done by sending a command in this format (ASCII characters):
MM PP\r
where MM is the test mode, PP is the PID, and \r is a carriage return (hex: 0x0d). All whitespace characters are ignored by the Kiwi. *Test modes 03 and 04 do not require a PID value.
For example, requesting current RPM is done as follows:
01 0C\r
The PID response from the Kiwi Wifi or Kiwi Bluetooth is in this format:
NN PP AA [BB] [...]
where the NN represents the test mode + 40 (e.g. 01 + 40 = 41). PP is the requested PID, and all following characters are data bytes.
The number of returned bytes is dependent on the particular PID requested. For details on PIDs supported by most vehicles and the number of returned bytes, please see "Requesting Data".
Here is an example response from the Kiwi Wifi after requesting the current RPM:
41 0C FF FF
The data bytes "FF FF" are ASCII representations of hexadecimal characters for the data. In this case, the "FF FF" would be interpreted as the hexadecimal value of 0xFFFF (65536 in decimal base). An example function for converting this value to meaningful data is outlined in Section 11.
Other responses are possible as well. A table of responses can be seen below:
|
Response
|
Description
|
|
?
|
Command not understood
|
|
BUFFER FULL
|
Internal buffer full
|
|
BUS ERROR
|
Invalid singal detected on bus
|
|
CAN ERROR
|
Unable to initialize, send or receive CAN data
|
|
DATA ERROR
|
Incorrect or invalid response from vehicle
|
|
NO DATA
|
No data response for request
|
|
OK
|
Command successful
|
|
SEARCHING...
|
Connecting to vehicle
|
|
UNABLE TO CONNECT
|
No valid OBD protocol found
|
iMFD Mode
Switching the Kiwi to iMFD mode will automatically read the serial data from any attached sensor modules. The data packet format for the iMFD serial stream is formatted as below:
Start Bit
/*Start first sensor*/
Sensor Address MSB (Bits 6-11)
Sensor Address LSB (Bits 0-5)
Sensor Instance
Sensor Data MSB (Bits 6-11)
Sensor Data LSB (Bits 0-5)
/*End first sensor*/
//Additional sensors/instances are included before the stop bit
Stop Bit
Please note that the two most significant bits of each packet is reserved for the start bit and the stop bit.
Start Bit = 0x80(hex) = 1000 0000 (binary)
Stop Bit = 0x40(hex) = 0100 0000 (binary)
The 6 least significant bits are reserved for Address, Instance, and Data. This means that the two most significant bits MUST BE ZERO for these bytes. To interpret the Sensor Address and Data Value a bitwise conversion must be done.
An example conversion for address bits and data bits is as follows:
addr = (addrmsb << 6) | addrlsb; //Use this for true address value
data = (datamsb << 6) | datalsb; //Use this for true data value
For multiple sensor modules, the Instance byte is automatically incremented by 1 for each sensor module of the same address in the chain. Here is an example of two SM-AFR sensor modules:
0x80 //Start bit
0x00 //First SM-AFR Address MSB
0x00 //First SM-AFR Address LSB
0x00 //First SM-AFR Instance 1
0x00 //First SM-AFR Data MSB
0x04 //First SM-AFR Data LSB
0x00 //Second SM-AFR Address MSB
0x00 //Second SM-AFR Address LSB
0x01 //Second SM-AFR Instance 2 //value incremented
0x00 //Second SM-AFR Data MSB
0x05 //Second SM-AFR Data LSB
0x40 //Stop bit
When iMFD mode is active, the Kiwi automatically incorporates a flow control to improve performance when writing applications for the iPhone or iPod touch. When the '-' character is sent, the hardware waits for the start bit to arrive and only passes one complete frame. It then waits indefinitely. A '+' followed by a carriage return is necessary to get back to OBD Mode.
Start bit
...
Stop bit
(waits indefinitely)
(send a '+' then carriage return then '-' to obtain the next frame)
*It is recommended that you send a carriage return (\r) character to obtain the '>' character in order for the "OBD mode" to be ready for its next command.
The flow control guarantees that the first iMFD byte that is transmitted back is a start bit and the last byte is a stop bit. One complete iMFD frame will be available each time the iMFD mode is activated.
Custom PIDs
Manufacturer-specific PIDs and custom PIDs are supported by the Kiwi Wifi and Kiwi Bluetooth.
Please note that manufacturer-specific information typically requires a licensing fee for code and/or algorithm access. PLX Devices cannot and will not provide any manufacturer-specific information.
Suggested Initialization Sequence
//C-pseudo code to reset device and read data
WriteTCP("atz\r"); //Resets device
WriteTCP("ate0\r"); //Turns echo off
Data = RequestPIDData(0x11, 1); //Request data from vehicle
if(PIDReadStatus == 2 | PIDReadStatus == 3) { //Check connection status
OBDConnected = 0;
} else { //Connected
OBDConnected = 1;
}
Requesting Data
|
Sensor
|
PID Value (Hex)
|
Returned bytes
|
|
*Absolute Throttle Position
|
11
|
1
|
|
*Engine RPM
|
0C
|
2
|
|
*Vehicle Speed
|
0D
|
1
|
|
*Calculated Load Value
|
04
|
1
|
|
*Timing Advance (Cyl#1)
|
0E
|
1
|
|
*Intake Manifold Pressure
|
0B
|
1
|
|
*Air Flow Rate (MAF Sensor)
|
10
|
2
|
|
*Fuel System Status
|
03
|
2
|
|
*Short Term Fuel Trim (Bank 1)
|
06
|
2
|
|
*Long Term Fuel Trim (Bank 1)
|
07
|
2
|
|
*Short Term Fuel Trim (Bank 2)
|
08
|
2
|
|
*Long Term Fuel Trim (Bank 2)
|
09
|
2
|
|
*Intake Air Temperature
|
0F
|
1
|
|
*Coolant Temperature
|
05
|
1
|
|
Fuel Pressure (gauge)
|
0A
|
1
|
|
*O2 Sensor 1, Bank 1
|
14
|
2
|
|
*O2 Sensor 2, Bank 1
|
15
|
2
|
|
O2 Sensor 3, Bank 1
|
16
|
2
|
|
O2 Sensor 4, Bank 1
|
17
|
2
|
|
O2 Sensor 1, Bank 2
|
18
|
2
|
|
O2 Sensor 2, Bank 2
|
19
|
2
|
|
O2 Sensor 3, Bank 2
|
1A
|
2
|
|
O2 Sensor 4, Bank 2
|
1B
|
2
|
|
Time Since Engine Start
|
1F
|
2
|
|
Fuel Level Input
|
2F
|
1
|
|
Barometric Pressure (Absolute)
|
33
|
1
|
|
Catalytic Converter Temp B1S1
|
3C
|
2
|
|
Catalytic Converter Temp B2S1
|
3D
|
2
|
|
Catalytic Converter Temp B1S2
|
3E
|
2
|
|
Catalytic Converter Temp B2S2
|
3F
|
2
|
|
ECU Voltage
|
42
|
2
|
|
Absolute Engine Load
|
43
|
2
|
|
Ambient Air Temperature
|
46
|
1
|
*Denotes sensor is available in most vehicles. Additional sensors are available depending on vehicle specific models.
//Bluetooth communication will require write(byte[]) and read(byte[]) instead of WriteTCP() and ReadTCP()
int RequestPIDData(int PID,int bytes) //Pseudo C Code Example
{
int lsb,msb;
char c;
int b0,b1,b2,b3,b4,b5,b6,b7;
int Data;
lsb = (PID & 0x0f);
msb = ((PID & 0xf0)>>4);
WriteTCP('0');
WriteTCP('1');
if(msb == 0)
WriteTCP('0');
else if(msb == 1)
WriteTCP('1');
else if(msb == 2)
WriteTCP('2');
else if(msb == 3)
WriteTCP('3');
else if(msb == 4)
WriteTCP('4');
else if(msb == 5)
WriteTCP('5');
else if(msb == 6)
WriteTCP('6');
else if(msb == 7)
WriteTCP('7');
else if(msb == 8)
WriteTCP('8');
else if(msb == 9)
WriteTCP('9');
else if(msb == 10)
WriteTCP('A');
else if(msb == 11)
WriteTCP('B');
else if(msb == 12)
WriteTCP('C');
else if(msb == 13)
WriteTCP('D');
else if(msb == 14)
WriteTCP('E');
else if(msb == 15)
WriteTCP('F');
if(lsb == 0)
WriteTCP('0');
else if(lsb == 1)
WriteTCP('1');
else if(lsb == 2)
WriteTCP('2');
else if(lsb == 3)
WriteTCP('3');
else if(lsb == 4)
WriteTCP('4');
else if(lsb == 5)
WriteTCP('5');
else if(lsb == 6)
WriteTCP('6');
else if(lsb == 7)
WriteTCP('7');
else if(lsb == 8)
WriteTCP('8');
else if(lsb == 9)
WriteTCP('9');
else if(lsb == 10)
WriteTCP('A');
else if(lsb == 11)
WriteTCP('B');
else if(lsb == 12)
WriteTCP('C');
else if(lsb == 13)
WriteTCP('D');
else if(lsb == 14)
WriteTCP('E');
else if(lsb == 15)
WriteTCP('F');
WriteTCP(0x0d);
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP();
if(c == 'N')
{
PIDReadStatus = 1; //No Data
//Wait for OK>
while(c != 0x3E)
{
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP();
}
return 0;
}
else if(c == 'S')
{
PIDReadStatus = 2; //Searching
//Wait for OK>
while(c != 0x3E)
{
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP();
}
return 0;
}
else if(c != '4')
{
PIDReadStatus = 3; //Anything else
//Wait for OK>
while(c != 0x3E)
{
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP();
}
return 0;
}
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP();
if(c != '1')
{
PIDReadStatus = 3; //Second character not 1
//Wait for OK>
while(c != 0x3E)
{
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP();
}
return 0;
}
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP(); //space
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP(); //msb
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP(); //lsb
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP(); //space
if(bytes == 1) //data
{
while(!DataRdyTCP());
b0 = ReadTCP();
while(!DataRdyTCP());
b1 = ReadTCP();
b0 = CharToInt(b0);
b1 = CharToInt(b1);
Data = (b0<<4) + b1;
PIDReadStatus = 0;
//Wait for OK>
while(c != 0x3E)
{
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP();
}
return Data;
}
else if(bytes == 2) //data
{
while(!DataRdyTCP());
b0 = ReadTCP();
while(!DataRdyTCP());
b1 = ReadTCP();
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP();
while(!DataRdyTCP());
b2 = ReadTCP();
while(!DataRdyTCP());
b3 = ReadTCP();
b0 = CharToInt(b0);
b1 = CharToInt(b1);
b2 = CharToInt(b2);
b3 = CharToInt(b3);
Data = (b0<<12) + (b1<<8) + (b2<<4) + b3;
PIDReadStatus = 0;
//Wait for OK>
while(c != 0x3E)
{
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP();
}
return Data;
}
else if(bytes == 4) //data
{
while(!DataRdyTCP());
b0 = ReadTCP();
while(!DataRdyTCP());
b1 = ReadTCP();
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP();
while(!DataRdyTCP());
b2 = ReadTCP();
while(!DataRdyTCP());
b3 = ReadTCP();
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP();
while(!DataRdyTCP());
b4 = ReadTCP();
while(!DataRdyTCP());
b5 = ReadTCP();
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP();
while(!DataRdyTCP());
b6 = ReadTCP();
while(!DataRdyTCP());
b7 = ReadTCP();
b0 = CharToInt(b0);
b1 = CharToInt(b1);
b2 = CharToInt(b2);
b3 = CharToInt(b3);
b4 = CharToInt(b4);
b5 = CharToInt(b5);
b6 = CharToInt(b6);
b7 = CharToInt(b7);
Data = (b0<<28) + (b1<<24) + (b2<<20) + (b3<<16) + (b4<<12) + (b5<<8) + (b6<<4) + b7;
PIDReadStatus = 0;
//Wait for OK>
while(c != 0x3E)
{
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP();
}
return Data;
}
}
int CharToInt(int c)
{
int i;
if(c == 48) //'0'
i = 0;
else if(c == 49) //'1'
i = 1;
else if(c== 50) //'2'
i = 2;
else if(c== 51) //'3'
i = 3;
else if(c== 52) //'4'
i = 4;
else if(c== 53) //'5'
i = 5;
else if(c== 54) //'6'
i = 6;
else if(c== 55) //'7'
i = 7;
else if(c== 56) //'8'
i = 8;
else if(c== 57) //'9'
i = 9;
else if(c== 65) //'A'
i = 10;
else if(c== 66) //'B'
i = 11;
else if(c== 67) //'C'
i = 12;
else if(c== 68) //'D'
i = 13;
else if(c== 69) //'E'
i = 14;
else if(c== 70) //'F'
i = 15;
return i;
}
Interpreting Returned Data
This function is used to convert the returned raw PID data into meaningful values.
//Pseudo C Code Example
int PIDConversion(int PID, int Data, int Units)
//Units parameter: 0 = Standard Units, 1 = Metric Units
{
double tempMPH;
if(PID == 0x11) //Throttle
return Data*100/255;
else if(PID == 0x0c) //RPM
return Data/4;
else if(PID == 0x0d) //Speed
{
if(Units == 0) // MPH
{
tempMPH = Data/1.609;
return(Round(tempMPH));
}
else
return Data; //KM/H
}
else if(PID == 0x04) //Engine Load
return Data*100/255;
else if(PID == 0x0E) //Timing Advance
{
if(Data < 128)
return (128 - Data)/2;
else
return (Data - 128)/2;
}
else if(PID == 0x0B) //Intake Manifold Pressure
{
if(Units == 0)
return Data/0.3386; //inHG
else
return Data; //Kpa
}
else if(PID == 0x10) //Air Flow Rate
{
if(Units == 0)
return Round(Data*0.013227736); //LBS/min
else
return Round(Data*0.01); //g/s
}
else if(PID == 0x03) //Fuel System Status
return (Data>>8) & 0xFF;
else if((PID == 0x06)|(PID == 0x07)|(PID == 0x08)|(PID == 0x09)) //Fuel TRIM
{
if(Data < 128)
return (128 - Data)*100/128;
else
return (Data - 128)*100/128;
}
else if((PID == 0x0F)|(PID == 0x05)) //AIT and Coolant
{
if(Units == 0) //Fahrenheit
{
if(Data < 40)
return 32;
else
return (Data-40)*9/5 + 32;
}
else //Celsius
{
if(Data < 40)
return 0;
else
return Data - 40;
}
}
else if(PID == 0x0A) //Fuel Pressure
{
if(Units == 0) //PSI
return Data*3*0.145;
else //KPA
return Data*3;
}
else if(PID == 0x1C) //OBD TYPE
return Data;
else if((PID == 0x14)|(PID == 0x15)|(PID == 0x18)|(PID == 0x19)) //O2 Voltage
return (Data >> 8)*0.5;
else if(PID == 0x2F) //Fuel Level Input
return Data*100/255;
else if(PID == 0x33) //Barometric Pressure
{
if(Units == 0)
return Data/0.3386; //inHG
else
return Data; //Kpa
}
else if((PID == 0x3C)|(PID == 0x3D)|(PID == 0x3E)|(PID == 0x3F)) //CAT Temperature
{
Data = Data*0.1;
if(Units == 0) //Fahrenheit
{
if(Data < 40)
return 32;
else
return (Data-40)*9/5 + 32;
}
else //Celsius
{
if(Data < 40)
return 0;
else
return Data - 40;
}
}
else if(PID == 0x42) //ECU Voltage
return Data*0.01;
else if(PID == 0x43) //ASB Engine Load
return Data*100/255;
else if(PID == 0x46) //Ambient Air Temperature
{
if(Units == 0) //Fahrenheit
{
if(Data < 40)
return 32;
else
return (Data-40)*9/5 + 32;
}
else //Celsius
{
if(Data < 40)
return 0;
else
return Data - 40;
}
}
else if(PID == 0x22) //FRP Rel
{
if(Units == 0)
return Data*0.79*0.145; //PSI
else
return Data*0.79; //Kpa
}
}
Reset Trouble Code
//Pseudo C Code Example
void ResetTroubleCode()
{
char c;
//Clear Input Buffer Here
//Reset Code
WriteTCP('0');
WriteTCP('4');
WriteTCP(0x0d);
//Wait for carriage return as precaution to system freeze.
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP();
//Wait for OK>
while(c != 0x3E)
{
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP();
}
}
Read Number of Trouble Codes
//Pseudo C Code Example
void RequestNumberTrouble()
{
char c;
//Clear Input Buffer Here
WriteTCP('0');
WriteTCP('1');
WriteTCP('0');
WriteTCP('1');
WriteTCP(0x0d);
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP();//4
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP();//1
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP();//space
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP();//0
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP();//1
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP();//space
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP();//0
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP();//number of error codes
errornumber = c;
//The return string is long so wait for carriage return or else system will freeze.
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP();
//Wait for OK>
while(c != 0x3E)
{
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP();
}
}
Request Trouble Code
//Pseudo C Code Example
void RequestTroubleCodes(int count) // Reads back 3 codes only.
{
int b0,b1,b2,b3; //Error 1
int b4,b5,b6,b7; //Error 2
int b8,b9,b10,b11; //Error 3
int c;
int x;
if(count == 0)
return;
//Clear Input Buffer Here
WriteTCP('0');
WriteTCP('3');
WriteTCP(0x0d);
//Non-CAN protocols
if(ConnectProtocol == 0)
{
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP(); //4
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP(); //3
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP(); //space
while(!DataRdyTCP());
b0 = ReadTCP(); //Error1
while(!DataRdyTCP());
b1 = ReadTCP(); //Error1
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP(); //space
while(!DataRdyTCP());
b2 = ReadTCP(); //Error1
while(!DataRdyTCP());
b3 = ReadTCP(); //Error1
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP(); //space
while(!DataRdyTCP());
b4 = ReadTCP(); //Error2
while(!DataRdyTCP());
b5 = ReadTCP(); //Error2
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP(); //space
while(!DataRdyTCP());
b6 = ReadTCP(); //Error2
while(!DataRdyTCP());
b7 = ReadTCP(); //Error2
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP(); //space
while(!DataRdyTCP());
b8 = ReadTCP(); //Error3
while(!DataRdyTCP());
b9 = ReadTCP(); //Error3
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP(); //space
while(!DataRdyTCP());
b10 = ReadTCP(); //Error3
while(!DataRdyTCP());
b11 = ReadTCP(); //Error3
}
else //CAN
{
if(count <= 2)
{
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP(); //4
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP(); //3
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP(); //space
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP(); //Number Trouble
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP(); //Number Trouble
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP(); //space
while(!DataRdyTCP());
b0 = ReadTCP(); //Error1
while(!DataRdyTCP());
b1 = ReadTCP(); //Error1
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP(); //space
while(!DataRdyTCP());
b2 = ReadTCP(); //Error1
while(!DataRdyTCP());
b3 = ReadTCP(); //Error1
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP(); //space
while(!DataRdyTCP());
b4 = ReadTCP(); //Error2
while(!DataRdyTCP());
b5 = ReadTCP(); //Error2
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP(); //space
while(!DataRdyTCP());
b6 = ReadTCP(); //Error2
while(!DataRdyTCP());
b7 = ReadTCP(); //Error2
}
else //3 or more trouble codes
{
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP();
//Wait for ':'
while(c != ':')
{
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP();
}
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP(); //space
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP(); //4
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP(); //3
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP(); //space
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP(); //Number Trouble
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP(); //Number Trouble
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP(); //space
while(!DataRdyTCP());
b0 = ReadTCP(); //Error1
while(!DataRdyTCP());
b1 = ReadTCP(); //Error1
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP(); //space
while(!DataRdyTCP());
b2 = ReadTCP(); //Error1
while(!DataRdyTCP());
b3 = ReadTCP(); //Error1
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP(); //space
while(!DataRdyTCP());
b4 = ReadTCP(); //Error2
while(!DataRdyTCP());
b5 = ReadTCP(); //Error2
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP(); //space
while(!DataRdyTCP());
b6 = ReadTCP(); //Error2
while(!DataRdyTCP());
b7 = ReadTCP(); //Error2
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP();
while(c != ':') //Wait for ':'
{
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP();
}
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP(); //space
while(!DataRdyTCP());
b8 = ReadTCP(); //Error3
while(!DataRdyTCP());
b9 = ReadTCP(); //Error3
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP(); //space
while(!DataRdyTCP());
b10 = ReadTCP(); //Error3
while(!DataRdyTCP());
b11 = ReadTCP(); //Error3
}
}
errb0 = b0;
errb1 = b1;
errb2 = b2;
errb3 = b3;
errb4 = b4;
errb5 = b5;
errb6 = b6;
errb7 = b7;
errb8 = b8;
errb9 = b9;
errb10 = b10;
errb11 = b11;
//For 4+ error codes - multiple lines are returned
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP();
//Wait for OK>
while(c != 0x3E)
{
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP();
}
}
void ErrorCodePrefix(int b0)
{
if(b0 == 0)
{
hc = '0';
thc = 'P';
}
else if(b0 == 1)
{
hc = '1';
thc = 'P';
}
else if(b0 == 2)
{
hc = '2';
thc = 'P';
}
else if(b0 == 3)
{
hc = '3';
thc = 'P';
}
else if(b0 == 4)
{
hc = '0';
thc = 'C';
}
else if(b0 == 5)
{
hc = '1';
thc = 'C';
}
else if(b0 == 6)
{
hc = '2';
thc = 'C';
}
else if(b0 == 7)
{
hc = '3';
thc = 'C';
}
else if(b0 == 8)
{
hc = '0';
thc = 'b';
}
else if(b0 == 9)
{
hc = '1';
thc = 'b';
}
else if(b0 == 10)
{
hc = '2';
thc = 'b';
}
else if(b0 == 11)
{
hc = '3';
thc = 'b';
}
else if(b0 == 12)
{
hc = '0';
thc = 'U';
}
else if(b0 == 13)
{
hc = '1';
thc = 'U';
}
else if(b0 == 14)
{
hc = '2';
thc = 'U';
}
else if(b0 == 15)
{
hc = '3';
thc = 'U';
}
}
int GetProtocol() //returns 1 for CAN, 0 for other
{
char c;
char s[15];
int x;
//Clear Input Buffer Here
WriteTCP('a');
WriteTCP('t');
WriteTCP('d');
WriteTCP('p');
WriteTCP(0x0d);
getsTCP (s, 15); //Get a string of 15 characters
//The return string is long so wait for carriage return or else system will freeze.
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP();
//Wait for OK>
while(c != 0x3E)
{
while(!DataRdyTCP());
c = ReadTCP();
}
for(x=0;x<11;x++)
{
if((s[x] == '1') & (s[x+1] == '5') & (s[x+2] == '7'))
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
PLX iMFD Sensor Table
|
Sensor
|
Address
|
Units
|
Min
|
Max
|
|
Wideband O2
|
0
|
0 - Lambda
|
0.68
|
1.36
|
|
|
|
1 - Gasoline (14.7)
|
10
|
20
|
|
|
|
2 - Diesel (14.6)
|
9.93
|
19.86
|
|
|
|
3 - Methanol (6.4)
|
4.35
|
8.7
|
|
|
|
4 - Ethanol (9.0)
|
6.12
|
12.24
|
|
|
|
5 - LPG (15.5)
|
10.54
|
21.08
|
|
|
|
6 - CNG (17.2)
|
11.7
|
23.39
|
|
|
|
7 - E85 (9.76)
|
6.64
|
13.27
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Exhaust Gas Temp
|
1
|
0 - Celsius
|
0
|
1023
|
|
|
|
1 - Fahrenheit
|
32
|
1873
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fluid Temp
|
2
|
0 - Celsius Water
|
0
|
150
|
|
|
|
1 - Fahrenheit Water
|
32
|
302
|
|
|
|
2 - Celsius Oil
|
0
|
150
|
|
|
|
3 - Fahrenheit Oil
|
32
|
302
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Vacuum
|
3
|
0 - Vac in/Hg
|
29.93
|
0
|
|
|
|
1 - Vac mm/Hg
|
760
|
0
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Boost
|
4
|
2 - Boost 0-30 PSI
|
0
|
30
|
|
|
|
3 - Boost 0-2 kg/cm
2
|
0
|
2.07
|
|
|
|
4 - Boost 0-15 PSI
|
0
|
15
|
|
|
|
5 - Boost 0-1 kg/cm
2
|
0
|
1.12
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Air Intake Temp
|
5
|
0 - Celsius
|
0
|
150
|
|
|
|
1 - Fahrenheit
|
32
|
302
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RPM
|
6
|
0 - 8k
|
0
|
8000
|
|
|
|
1 - 12k
|
0
|
12000
|
|
|
|
2 - 20k
|
0
|
20000
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Speed
|
7
|
0 - MPH
|
0
|
160
|
|
|
|
1 - km/H
|
0
|
258
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Throttle Position
|
8
|
0 - Percent
|
0
|
100
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Engine Load
|
9
|
0 - Percent
|
0
|
100
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fluid Pressure
|
10
|
0 - PSI Fuel
|
0
|
120
|
|
|
|
1 - kg/cm
2 Fuel
|
0
|
8.44
|
|
|
|
2 - Bar Fuel
|
0
|
8.27
|
|
|
|
3 - PSI Oil
|
0
|
120
|
|
|
|
4 - kg/cm
2 Oil
|
0
|
8.44
|
|
|
|
5 - Bar Oil
|
0
|
8.27
|
|
Sensor
|
Address
|
Units
|
Min
|
Max
|
|
Timing
|
11
|
0 - Degree
|
-64
|
64
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Manifold Absolute
|
12
|
0 - kPa
|
0
|
255
|
|
Pressure (MAP)
|
|
1 - inHg
|
0
|
75.3
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Mass Air Flow (MAF)
|
13
|
0 - g/s
|
0
|
655.35
|
|
|
|
1 - lb/min
|
0
|
86.69
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Short Term Fuel Trim
|
14
|
0 - Percent
|
-100
|
100
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Long Term Fuel Trim
|
15
|
0 - Percent
|
-100
|
100
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Narrowband O2
|
16
|
0 - Percent
|
0
|
100
|
|
|
|
1 - Volts
|
0
|
1.275
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fuel Level
|
17
|
0 - Percent
|
0
|
100
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Volt Meter
|
18
|
0 - Volts
|
0
|
20
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Knock
|
19
|
0 - Volts
|
0
|
5
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Duty Cycle
|
20
|
0 - Positive
|
0
|
100
|
|
|
|
1 - Negative
|
0
|
100
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fuel Efficiency
|
21
|
0 - MPG
|
0
|
100
|
|
|
|
1 - KM/L
|
0.43
|
42.51
|
|
|
|
2 - L=100KM
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Analog Voltage
|
22
|
0 - Volts
|
0
|
5
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Speed (Hertz)
|
23
|
0 - Hz
|
0
|
10,230
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Wideband AFR Status
|
24
|
0 - Heating, Ready
|
0
|
1
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Wideband AFR Health
|
25
|
0 - Percent
|
0
|
101
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Wideband AFR Reaction
|
26
|
0 - ms
|
0
|
999
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|